Circle Divide
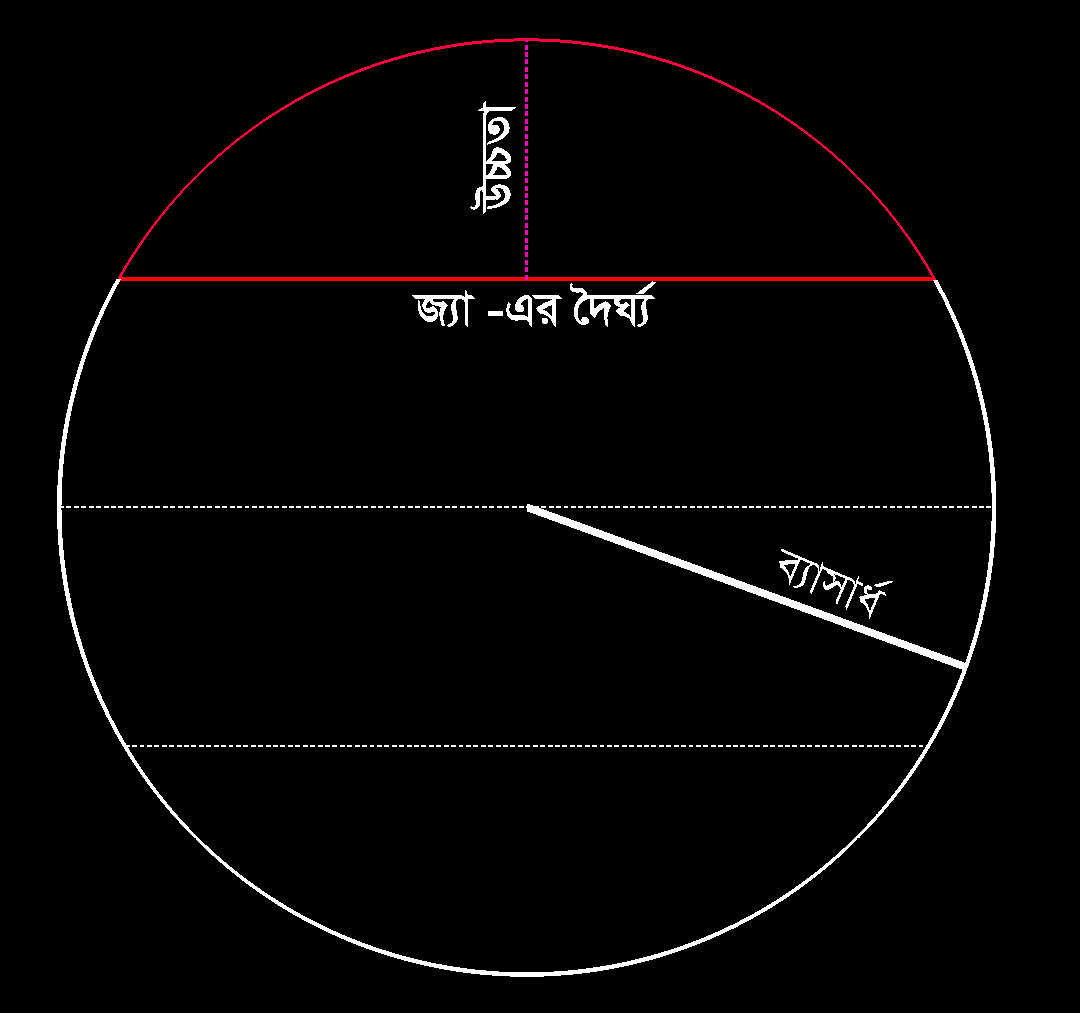
এখানে যে যে সূত্র ব্যাবহার হয়েছে:
-
To find the value of $\theta$ from the non-convertible implicit function:
\[
\text{Segment Area:} \quad A_{\text{segment}} = \frac{1}{2}r^2(\theta - \sin\theta)
\]
We used the Newton-Raphson method. The iterative formula for Newton's method is:
\[
\theta_{n+1} = \theta_n - \frac{f(\theta_n)}{f'(\theta_n)}
\]
where $f(\theta)$ is the given function, and $f'(\theta)$ is its derivative.
For $f(\theta) = A_{\text{segment}} - \frac{1}{2}r^2(\theta - \sin\theta)$, the derivative is:
\[
f'(\theta) = \frac{d}{d\theta} \left( A_{\text{segment}} - \frac{1}{2}r^2(\theta - \sin\theta) \right)
\]
To find the derivative, apply the chain rule:
\[
f'(\theta) = \frac{d}{d\theta} A_{\text{segment}} - \frac{d}{d\theta} \frac{1}{2}r^2(\theta - \sin\theta)
\]
After differentiation and simplification, we get:
\[
f'(\theta) = r^2\left(1 - \cos\theta\right)
\]
Now, we can iterate using the Newton-Raphson formula until convergence:
\[
\theta_{n+1} = \theta_n - \frac{A_{\text{segment}} - \frac{1}{2}r^2(\theta_n - \sin\theta_n)}{r^2\left(1 - \cos\theta_n\right)}
\]
For more details on Newton's method, you can visit Click Here
For a visual demonstration, you can watch the following YouTube video: Click Here
অথবা, এতো কিছু বাদ দিয়ে calculator ব্যাবহার করেন
- Area of a circle: \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times R^2 \] Where: \[ R = \text{radius} \] \[ D = \text{diameter} = 2 \times R \] \[ P = \text{perimeter} = 2 \times \pi \times R \]
- \[ \text{Radius, r} = \frac{c^2}{8h_{\text{segment}}} + \frac{h_{\text{segment}}}{2} \] \[ \text{Segment Area:} \quad A_{\text{segment}} = \frac{1}{2}r^2(\theta - \sin\theta) \] \[ \text{Segment Height:} \quad h_{\text{segment}} = r - \sqrt{r^2 - \left(\frac{c}{2}\right)^2} \] \[ \text{Chord Length:} \quad c = 2r\sin\left(\frac{\theta}{2}\right) \] \[ \text{Arc Length:} \quad s = r\theta \] \[ \text{Sector Area:} \quad A_{\text{sector}} = \frac{1}{2} r^2 \theta \]